Household Electricity
Household Electricity: Overview
This topic explains how current flows in an electric circuit and how to check whether the circuit is properly connected. It also covers the meaning of fuse bulbs.
Important Questions on Household Electricity
How is power transmitted from the power generating station to the consumer?
What is the transmission system in power system?
How is power transmitted to the transmission?
How is power transmitted from the power generating station to the consumer?
What is the power rating of electric bulb?
State whether the given statement is True or False :
Kilowatt hour is the unit of power.
Which of the following is an integrating instrument from below:
How is power transmitted from the power generating station to the consumer?
Electricity usage of the house is measured by _____.
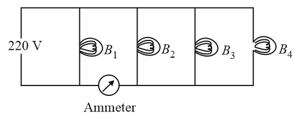
Four bulbs , , and of each are connected to main as shown in the figure. The reading in an ideal ammeter will be
The electricity supplied to a household by a substation is called the mains supply.
Which one of the following is not a step in the distribution process of electricity?
Correct power rating of bulb used in our country (India):
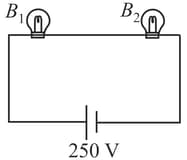
Bulb and bulb are connected across . What is potential drop across ?
If voltage across a bulb rated drops by of its rated value, the percentage of the rated value by which the power would decrease is
Incandescent bulbs are designed keeping in mind that the resistance of their filament increases with the increase in temperature. If at the room temperature , and bulbs have filament resistances , and respectively, then the relation between these resistances is
